Four key ways to secure your network
Your network contains resources and valuable information. We need to ensure that the right people have the required access to those resources. Learn 4 easy ways to keep your network secure
Being able to secure your network requires planning. You need to take into account how your business uses the network and what tools are available to provide security.
A balance has is required between being able to use the network and keeping it secure. Convenience and security are opposed to each other. More convenience often leads to lower security.
In this article, we will be highlighting four key ways to secure your network. Network architecture is divided into different functional groups or layers. The size and use of your network will affect which layers are used.
Here are the typical layers
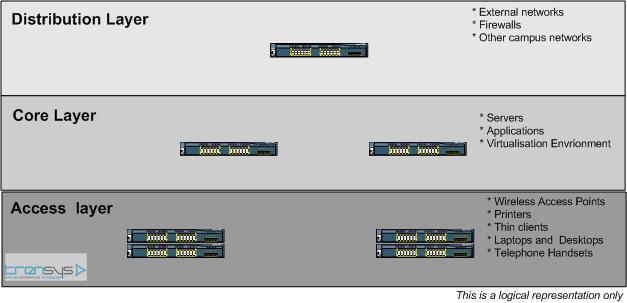
Not every network has all three layers. Some may have a mixture or all three all in one layer combined. The access layer is where your users plug into the network and is the biggest layer of your network.
We will focus on the top four ways to secure your network or access layer network.
What are the some of the threats?
Unidentified users and devices
Your network contains resources and valuable information. We need to ensure that the right people have the required access to those resources. With the increase in mobile computing and users utilise multiple devices to access your network. You need to ensure that the correct authorised device is connected to your network.
An un-authorised device on your network could contain and propagate malware or disrupt the functioning of your network. Therefore, the user and the device need to be authenticated.
Disruption and Denial of service
There are tools, which are freely available on the internet designed to break your network. They are designed to cause disruption or enable access to resources which the user is not authorised to access.
Securing user data
Most of the threats we have discussed so far are about protecting the resources on the network. The users also need protection from each other. Man in the middle (MITM) attacks occur where a user is tricked into divulging secure information via an un-authorized 3rd party.
Four key ways to secure your network.
Now we understand how the network is structured, and also what the threats are, let’s identify the top four ways to protect ourselves. This is not a how-to document, the aim is to provide you with a overview of how to protect yourself from the most common threats.
(1) 802.1x
802.1x is a standard developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Standards Association (IEEE). This standard defines the protocol and methods used to provide device and user authentication.
801.1x ensures that only the authorised users and devices get access to your network. When combined with Microsoft Network Policy server, Active Directory, LDAP and Radius.
Using these tools, you can ensure that the correct users and devices get access to your network.
Enabling 802.1x does reduce operational convenience. Your network administration now requires that you have a process to manage the policy of access, as well as maintain the list of authorised users and devices. This has to be performed effectively to ensure that users who have left the company or devices that are lost or stolen are removed quickly.
(2) DHCP Snooping
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) enables users to be automatically configured to operate on the network. Looking at our diagram highlighting the layers of the network, we will see that our servers and applications reside on the core network.
Therefore all the servers which perform Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol will also reside in the core network. We should not see any DHCP servers residing on the access layer. Access layer is where our users reside.
DHCP is often used as the first stage in a Man In the Middle (MITM) attack. Any user that has access to the network can setup a DHCP server to trick your users to use the configuration that they provide, instead of your DHCP servers.
To protect your network from unauthorised DHCP servers we need to listen to the network and disable these servers when if we see them.
DHCP Snooping does just this. It is configured on your network switches and it will shutdown any ports where it see’s any DHCP servers which you have not authorised. You can tell the switches that the only authorised servers are in the core network. Any other DHCP servers should be disabled.
(3)MAC Address limits
Every device that connects to a network has a Media Access Control (MAC) address. Think of it as a unique serial number. When you connect a device to a network switch it learns the MAC address of your device, and it learns which port the device is using.
A user port will typically have two devices per port. Most deployments will have a desktop pc and a telephone handset connected to the same port on the switch.
This means that the switch will see two MAC address’s. Anything more than two devices means that we are connecting switches together or something suspicious may be occurring on the port.
If it is abnormal for a user to have more than two devices per port, you can tell the switch to shutdown the port whilst you investigate what is occurring.
(4) Physical port security
Physical port security is one of the easiest forms of security for your network. By taking out the cable or disabling the network port when not in use takes away any form of un-authorised access. You also do not need any special features on your switch to perform physical access controls.
A key point to remember is that this needs to be part of your administration process, otherwise it will become a burden.
Summary
We have highlighted four key ways to secure your user network. Which ones you use depends on your exposure to threat. If your network is in a building with strong access controls and your network switches are in locked physical cabinets, you could say that your threat level is quite low and you may only use Physical port security.
If your network resides in a school/college or serviced office, you may need to consider using all forms of security.
When choosing network equipment it is important to have an understanding that not every network switch is the same.The network access layer switches will be the most abundant type of switch. It is also for this reason that most business owners will look for the cheapest possible switch with minimal regard for functionality.
Where possible stay away from the “Small Business” switches or the “Smart Managed” switches. These switches are often the most constrained feature less switches, which are only suitable for small work-groups.
Key features to look for when looking for access layer switches:
• IEEE 802.1x
• Port Security
• MAC authentication
• MAC address limit
• Layer 2 MAC filtering
• Layer 3 IP filtering
• Layer 4 TCP/UDP socket filtering
• BPDU guard
• Static MAC forwarding
• Multiple RADIUS servers
• Multiple TACACS+ servers
• RADIUS
• TACACS+
• SSL
• DHCP snooping
• ARP inspection
• UPNP
• Policy-based security filtering
• Port isolation
• IP source guard
• ACL packet filtering